
By Aaron Tay, Lead, Data Services
SMU Librarians have always assisted students and researchers in literature review, supporting users with advice on advanced Boolean searching, appropriate choice of sources and tools and tricks for searching and extracting references efficiently. However, with the growing complexity of the research environment and the need to provide more in-depth and specialized support in this growing area, SMU Libraries launched a new pilot Literature and Systematic review support service in Aug 2023.
To date, the team, lead by Aaron Tay, Lead Data Services, has provided in-depth literature review support in the following three main areas:
- Evidence synthesis support
- Bibliometric Analysis or Bibliometric review
- Various literature review tasks and workflows e.g. Workflows for bulk extraction of references, bulk cleaning of data, efficiently collaborating across multiple partners and more
In summary, our team goes beyond standard literature review support, offering two levels of service:
- Research consultant (lesser degree of involvement)
- Collaborator or co-author (higher degree of involvement, with conditions apply)
You can find more details about the Literature and Systematic Review Support Service from the Libraries' website.
A) Evidence synthesis support and less structured reviews and surveys
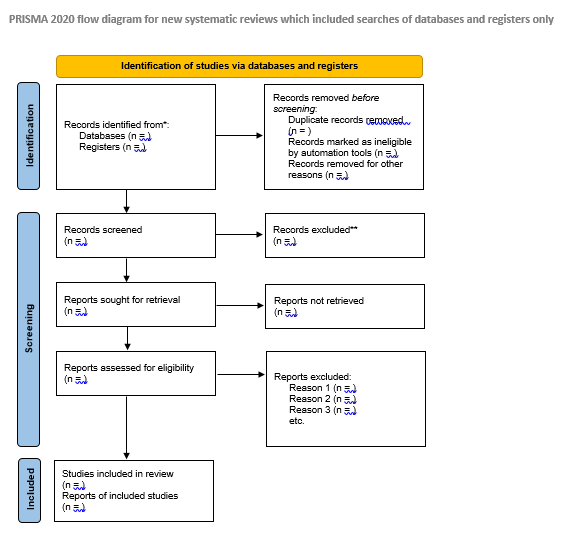
What is it: The idea of evidence synthesis, which encompasses systematic reviews, meta-analysis and less commonly known reviews like mapping reviews, umbrella reviews, focuses on the comprehensive and systematic gathering, analyzing, and summarizing of findings from various studies, reports, and data sources to address a specific research question or topic area. This started first in the clinical science (the most common standard used is Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions) areas but has since expanded to the fields of education, economics and even business and management.
How we help:
- Provide guidance on the use of specific methodologies and conducting standards (e.g., Cochrane Collaboration, Campbell Collaboration, Collaboration for Environmental Evidence etc.)
- Recommend databases and other sources for specific disciplines*
- Design and implement comprehensive and reproducible search strategies (including specific filters by journal titles) for multiple databases*
- Provide guidance on efficient bulk extraction and deduplication of search records found
- Recommend and assist in the use of other software to aid with the literature review process including:
- Covidence+ (Systematic review management)
+ Please email SMU Libraries to request for access to Covidence - ASreview (Semi-automated screening)
- Zotero (Deduplication)
- Various tools for citation chasing and other supplementary search methods
- Covidence+ (Systematic review management)
- Assist with best practices for reporting and documentation (e.g., PRISMA 2020 reporting standards)
Typical use case: We recently provided support to an MSE student conducting meta-analysis in the research area of health economics. Our assistance included conducting a preliminary exploration to identify relevant literature, such as other systematic reviews. We also aided in translating search strategies for compatibility with database platforms at SMU (e.g. PsycINFO on Ebsco vs OVID) and offered guidance on adhering to Cochrane protocols.
B) Bibliometric Analysis or Bibliometric review
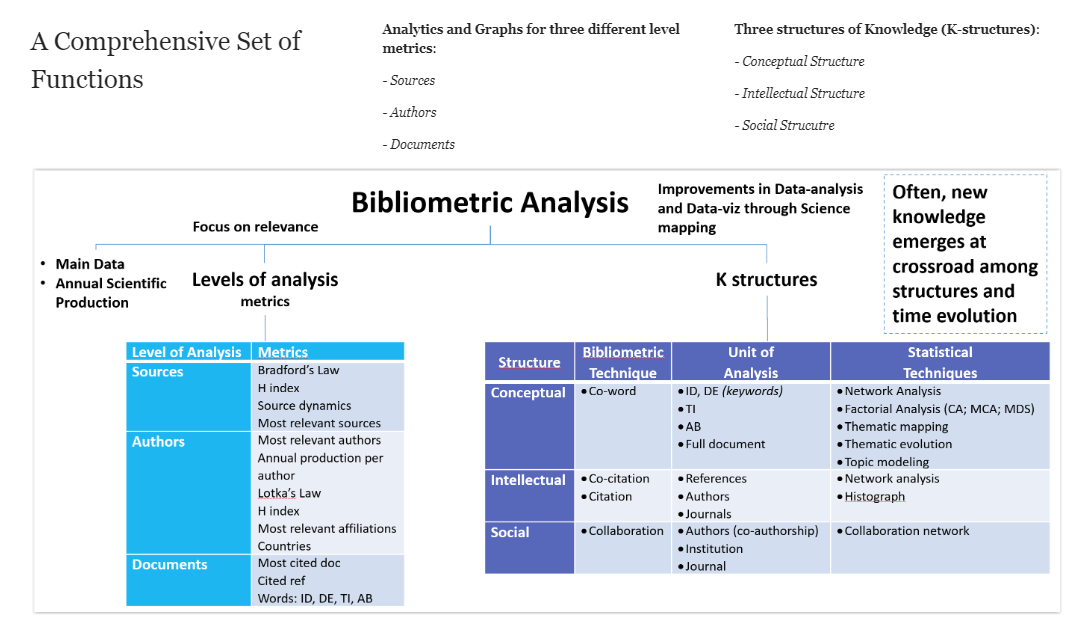
What is it: A bibliometric review, also known as bibliometric analysis, is a form of review where a researcher collects many relevant papers (typically ranging from a few hundred to several thousand) within a research area of interest. Subsequently, the researcher conducts a bibliometric analysis utilising data sourced from a citation database such as Scopus or Web of Science.
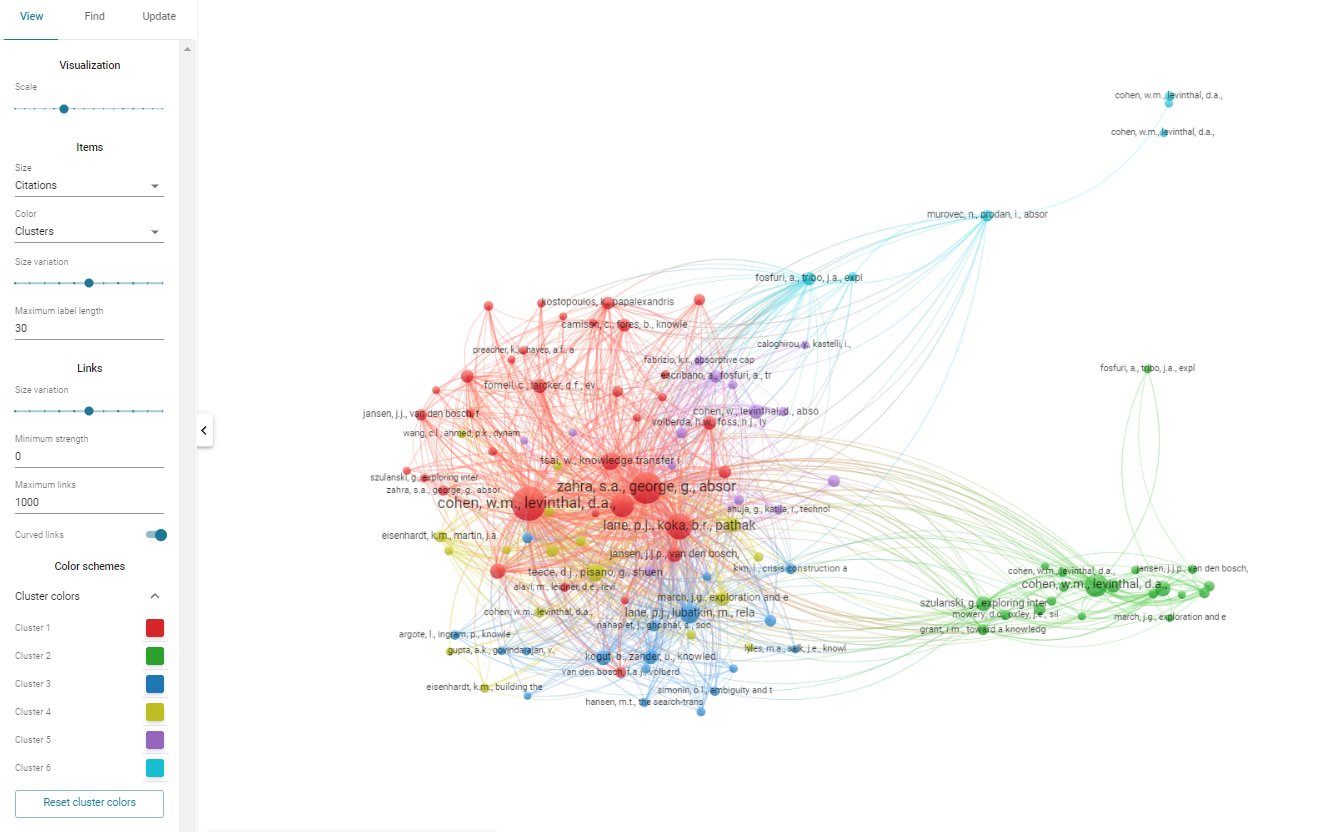
Broadly speaking, this analysis involves the use of visualization tools such as VOSviewer, CiteSpace, Biblimetrix, among others, to “uncover emerging trends in article and journal performance, collaboration patterns, and research constituents, and to explore the intellectual structure of a specific domain in the extant literature” (Donthu et al., 2021, p. 285).
You can find an example of such a paper by an SMU author here.
How we help:
- Guidance and assistance on widely used tools for bibliometric reviews, including VOSviewer, Bibliometrix/Biblishiny, Harzing’s Publish or Perish, Citespace
- Guidance for conducting bibliometric reviews and analyses within specific subfields
- Providing direction on academic search databases that are compatible with the aforementioned bibliometric tools
Typical use case: We offer expertise to researchers who are new to conducting bibliometric reviews or analyses and require assistance in understanding the process or utilizing relevant tools.
C) General structured bulk extraction for literature review tasks
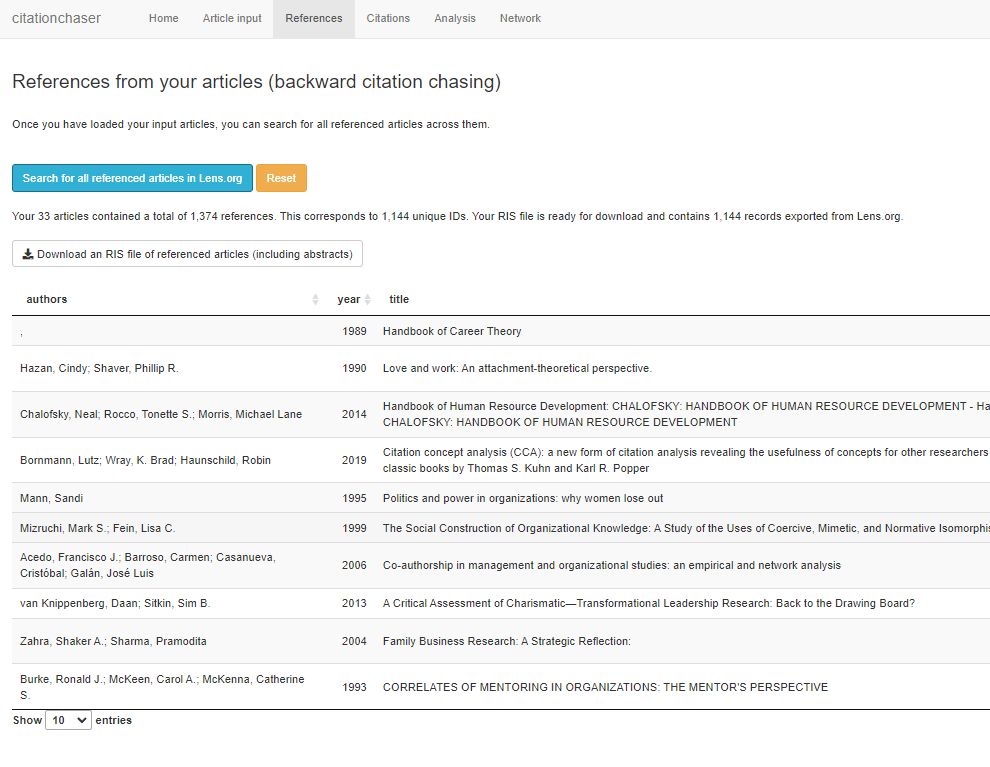
What is it: We recognise that not every literature review requires a comprehensive formal evidence synthesis. However, many can still benefit from more efficient literature review methods, particularly in bulk searching and extraction.
Have 20 relevant papers and wish to conduct a bulk extraction of references AND citations while removing duplicates to screen for relevant papers? Or perhaps you aim to do the same for papers that have citations or relevance two hops away? Need advice on how to efficiently clean up metadata in bulk? What is the best approach for collaboration across multiple authors? Is it possible to set up alerts based on AI-generated summaries? These are just a few examples of the assistance we have provided.
How we help:
- Expertise and knowledge of skills to help advise on the best literature review workflow
- Bulk extraction and dedupe of core papers in a specific research area
- Clean-up of inaccurate or missing metadata
- Advice on workflow for collaboration between multiple authors
- Questions regarding emerging AI-powered search tools like Elicit.com
Typical use case: Our service so far seems to be in demand among researchers engaged in interdisciplinary research where literature review can be more challenging, and a more systematic structured way of searching is needed to cover all bases.
Conclusion
If you are interested in finding out more, feel free to reach out to the Libraries for additional inquiries regarding the Literature and Systematic Review pilot service. Best of luck with your literature review!
References
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of business research, 133, 285-296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070